I am recently developing a new package simplifyEnrichment which clusters GO terms into clusters and visualizes the summaries of GO terms in each cluster as word cloud. The results are visualized by ComplexHeatmap where the word clouds are the heatmap annotations. In this post, I will describe how to implement word clouds as the heatmap annotation by ComplexHeatmap.
To achieve this, we need two functionalities: one draws the word cloud and one
links the word cloud to the corresponding rows in the heatmap. The former is
done with the word_cloud_grob() function that I will describe later and the
latter is done with anno_link() function which is already defined in
ComplexHeatmap package.
The word_cloud_grob() function is from simplifyEnrichment package and it,
as well as several related functions, can be directly sourced from
this Gist by
the following command:
source("https://gist.githubusercontent.com/jokergoo/bfb115200df256eeacb7af302d4e508e/raw/14f315c7418f3458d932ad749850fd515dec413b/word_cloud_grob.R")There are four functions defined in the script:
word_cloud_grob(): The main function that constructs the word cloud grob.widthDetails.word_cloud(): Helper function which returns the width of the word cloud grob bygrobWidth()function.heightDetails.word_cloud(): Helper function which returns the height of the word cloud grob bygrobHeight()function.scale_fontsize(): This function maps the word frequency to font size.
In the following parts of this post, I first describe how to set different parameters for constructing the word cloud grob, then demonstrate how to link the word cloud to the heatmap. Finally I reproduce the GO similarity heatmap that is generated with simplifyEnrichment package.
Word cloud grob
To demonstrate word_cloud_grob() function, I randomly generate a vector of
words and their font sizes.
set.seed(123)
words = sapply(1:30, function(x) strrep(sample(letters, 1), sample(3:10, 1)))
fontsize = runif(30, min = 5, max = 30)The words and the corresponding font sizes should be specified as in following code.
library(grid)
gb = word_cloud_grob(words, fontsize = fontsize, max_width = unit(100, "mm"))
grid.newpage()
grid.draw(gb)
grid.rect(width = grobWidth(gb), height = grobHeight(gb), gp = gpar(fill = NA))
The word cloud is very basic. The words are ordered by the font sizes and are
placed from the bottom to top. Words are assigned with random colors. There is
a box that contains the word cloud. Here max_width argument controls the
“maximal width” of the box. Note the final grob width returned by
grobWidth(gb) might be a little bit smaller than the value specified with
max_width because if the next word exceeds the box, it will be places into the
next line in the box. I draw the border of the grob explicitly so that you can
see the size of the grob.
If the width of the box changes, the height of the box changes accordingly. In the following example, the width is reduced to 60mm and you can see the box gets higher.
gb = word_cloud_grob(words, fontsize = fontsize, max_width = unit(60, "mm"))
grid.newpage()
grid.draw(gb)
grid.rect(width = grobWidth(gb), height = grobHeight(gb), gp = gpar(fill = NA))
The colors of words help to distinguish between the words. The col argument can
be set as a vector with the same length as the words.
# color as a vector
gb = word_cloud_grob(words, fontsize = fontsize, max_width = unit(100, "mm"), col = 1:30)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(gb)
grid.rect(width = grobWidth(gb), height = grobHeight(gb), gp = gpar(fill = NA))
col can also be set as a color mapping function that maps from font sizes
to colors. The color mapping function takes the fontsize vector as input and
returns the corresponding colors.
# color as a function
library(circlize)
col_fun = colorRamp2(c(5, 17, 30), c("blue", "black", "red"))
gb = word_cloud_grob(words, fontsize = fontsize, max_width = unit(100, "mm"),
col = col_fun)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(gb)
grid.rect(width = grobWidth(gb), height = grobHeight(gb), gp = gpar(fill = NA))
Other arguments in word_cloud_grob are line_space that controls the space
between lines and word_space that controls the space between words.
As a heatmap annotation
anno_link() function links a subset of rows in the heatmap to an external viewport.
The viewport that links to the heatmap should have fixed width and height. If the
word cloud is taken as the annotation, the size of the viewport relates to
the size of the word cloud grob. In the next code, I generated a word cloud
grob and calcualte their height and width.
gb = word_cloud_grob(words, fontsize = fontsize, max_width = unit(100, "mm"))
gb_h = grobHeight(gb)
gb_w = grobWidth(gb)I generate a random heatmap with 10 rows and 10 columns without row clustering, so that I can correspond the word cloud to the first three rows in the heatmap.
library(ComplexHeatmap)
m = matrix(rnorm(100), 10)
ht = Heatmap(m, cluster_rows = FALSE)What to draw in the “linking viewport” should be manually defined. In the
case here, I simply draw the word cloud by grid.draw(gb). I additionally
draw the background of the word cloud in light grey.
panel_fun = function(index, nm) {
grid.rect(gp = gpar(fill = "#EEEEEE", col = NA))
grid.draw(gb)
}anno_link() is set as follows. Note I also set the background color for the
“linking line” same as the background of the word cloud.
ht + rowAnnotation(word_cloud = anno_link(align_to = 1:3, which = "row",
panel_fun = panel_fun, size = gb_h,
width = gb_w + unit(5, "mm"), # the link is 5mm
link_gp = gpar(fill = "#EEEEEE", col = NA)
))
Ok, this is the simplest implementation of the word cloud annotation. To make it look nicer, you need to do a lot of manual adjustment. In the next section, I demonstrate how to make a nicer plot.
A real-world example
In this section, I reproduce the plot generated from simplifyEnrichment package. First I load some data objects:
tmp_file = tempfile()
download.file("https://jokergoo.github.io/word_cloud_annotation_example.RData",
destfile = tmp_file, quiet = TRUE)
load(tmp_file); file.remove(tmp_file)There are following three objects:
matA GO similarity matrix from 500 GO terms. Values are between 0 and 1 where 1 means exactly the same and 0 means completely different.clThe clustering labels of the 500 GO terms.keywordsA list of keywords and their frequencies extracted from the GO names in the corresponding GO cluster.
The data structure or the values of the three objects are as follows:
mat[1:6, 1:6]## GO:0046654 GO:0060003 GO:0019918 GO:0006051 GO:0038016 GO:0045060
## GO:0046654 1.00000000 0.0000000 0.18082993 0.08979910 0.09389934 0.01450020
## GO:0060003 0.00000000 1.0000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.19300314 0.00000000
## GO:0019918 0.18082993 0.0000000 1.00000000 0.08408824 0.12754833 0.01349981
## GO:0006051 0.08979910 0.0000000 0.08408824 1.00000000 0.07906032 0.00000000
## GO:0038016 0.09389934 0.1930031 0.12754833 0.07906032 1.00000000 0.01262854
## GO:0045060 0.01450020 0.0000000 0.01349981 0.00000000 0.01262854 1.00000000cl## [1] 1 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 1 5 1 1 5 4 5 6 6 3 3 5 3 3 3 1 3
## [26] 2 3 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 6 1 5 0 6 1 1 0 1 1 3 3 6
## [51] 1 5 3 6 3 2 2 1 3 3 0 2 3 3 2 6 11 5 2 3 0 4 5 1 13
## [76] 3 2 1 5 3 1 6 6 3 1 3 1 6 1 3 1 1 11 2 3 0 1 1 1 1
## [101] 3 2 1 1 2 15 1 16 2 5 1 0 13 5 1 6 5 5 5 0 3 1 3 1 3
## [126] 6 2 6 1 3 3 3 3 2 6 1 1 1 3 11 5 5 3 1 5 1 1 3 3 3
## [151] 1 1 3 2 3 3 0 2 1 1 2 5 0 2 6 1 5 1 1 6 5 2 0 3 15
## [176] 3 1 1 5 0 0 16 5 2 1 5 2 1 2 1 3 1 2 3 13 3 3 3 3 5
## [201] 1 1 4 3 2 6 5 1 3 3 3 3 3 1 6 1 6 3 6 3 3 5 3 3 6
## [226] 5 1 2 2 0 1 15 3 1 2 3 6 5 3 2 0 2 0 1 3 1 1 1 5 2
## [251] 1 3 0 3 3 3 15 6 1 1 2 5 3 3 5 5 5 5 2 2 1 5 3 6 1
## [276] 3 13 3 1 5 5 1 5 1 0 5 3 5 2 1 5 3 1 3 1 13 3 5 3 11
## [301] 3 1 2 1 2 15 6 15 2 3 6 4 3 5 1 1 13 3 1 1 3 0 5 1 5
## [326] 2 5 3 3 2 2 1 0 3 5 3 5 0 6 5 0 2 5 2 5 2 1 1 16 6
## [351] 1 1 11 5 1 1 2 5 5 2 2 6 1 3 0 13 2 3 6 1 1 1 2 6 1
## [376] 5 2 5 0 5 3 1 0 3 5 3 5 5 3 6 5 5 3 0 16 3 3 2 1 1
## [401] 2 3 4 0 3 1 1 1 16 0 1 3 3 3 5 0 2 0 6 3 1 2 1 1 5
## [426] 3 2 16 2 2 6 5 3 0 3 5 0 2 5 6 3 5 1 3 3 5 3 5 1 5
## [451] 3 2 15 2 2 5 5 5 3 1 3 4 3 3 0 1 5 1 0 3 3 1 5 3 2
## [476] 1 3 1 3 1 2 3 1 4 1 0 2 3 16 2 1 3 1 5 3 2 1 6 2 1
## Levels: 1 3 5 2 6 4 13 15 16 11 0keywords## $`1`
## word freq
## process process 60
## regulation regulation 47
## biosynthetic biosynthetic 25
## metabolic metabolic 20
## negative negative 15
## positive positive 13
## catabolic catabolic 13
## activity activity 11
## transcription transcription 10
## histone histone 8
##
## $`3`
## word freq
## regulation regulation 40
## cell cell 38
## development development 28
## differentiation differentiation 22
## positive positive 20
## involved involved 14
## morphogenesis morphogenesis 11
## negative negative 10
## formation formation 7
## production production 7
##
## $`5`
## word freq
## response response 39
## regulation regulation 25
## signaling signaling 24
## pathway pathway 21
## cellular cellular 19
## receptor receptor 11
## negative negative 9
## cell cell 7
## positive positive 7
## stimulus stimulus 6
##
## $`2`
## word freq
## transport transport 24
## regulation regulation 23
## secretion secretion 12
## ion ion 8
## localization localization 7
## negative negative 6
## transmembrane transmembrane 6
## vesicle vesicle 6
## positive positive 6
## cell cell 5
##
## $`6`
## word freq
## regulation regulation 17
## assembly assembly 10
## organization organization 7
## cell cell 6
## mitotic mitotic 6
## positive positive 6
## cycle cycle 5
## negative negative 3
## complex complex 3
## transition transition 3
##
## $`4`
## word freq
## apoptotic apoptotic 6
## process process 6
## regulation regulation 6
## cell cell 3
## positive positive 3
## negative negative 2
## death death 2
##
## $`13`
## word freq
## proliferation proliferation 6
## regulation regulation 6
## positive positive 5
## cell cell 3
## muscle muscle 2
##
## $`15`
## word freq
## viral viral 4
## regulation regulation 3
## complex complex 2
## host host 2
## replication replication 2
##
## $`16`
## word freq
## regulation regulation 5
## cell cell 4
## adhesion adhesion 4
## negative negative 3
## positive positive 2
##
## $`11`
## word freq
## regulation regulation 5
## negative negative 3
## binding binding 3
## activity activity 2
## positive positive 2
##
## $`0`
## word freq
## regulation regulation 16
## positive positive 11
## negative negative 4
## antigen antigen 4
## assembly assembly 3
## homeostasis homeostasis 3
## calcium calcium 3
## ion ion 3
## cell cell 3
## presynapse presynapse 2I first define the similarity heatmap. The settings can be very straightforwardly understood from the argument names.
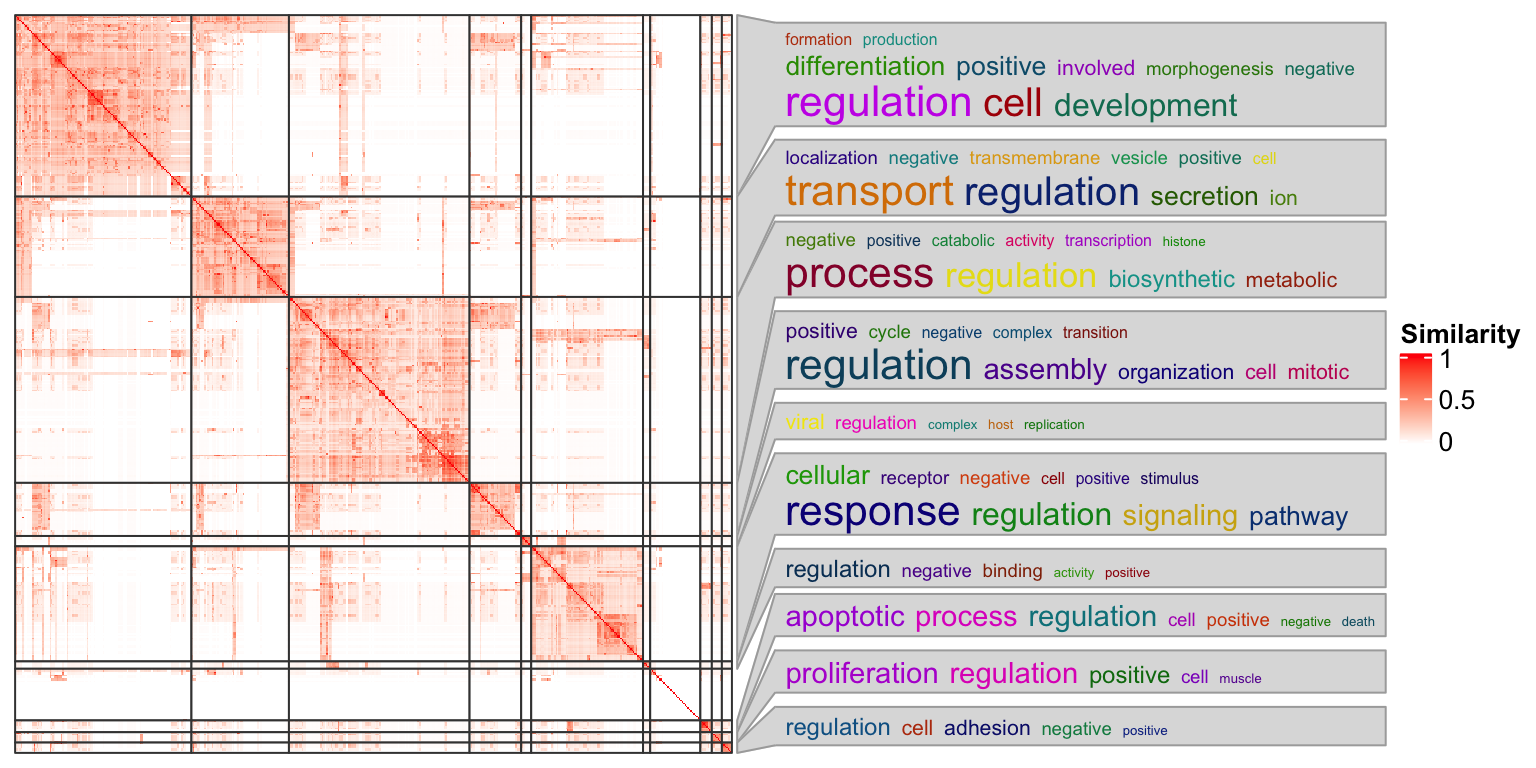
ht = Heatmap(mat, col = colorRamp2(c(0, 1), c("white", "red")),
name = "Similarity",
show_row_names = FALSE, show_column_names = FALSE,
show_row_dend = FALSE, show_column_dend = FALSE,
row_split = cl, column_split = cl,
border = "#404040", row_title = NULL, column_title = NULL,
row_gap = unit(0, "mm"), column_gap = unit(0, "mm"))There will be word clouds for every GO cluster, and since the GO terms are
split by cl, the “alignment variable” is defined as follows. The GO cluster
with label “0” is removed.
align_to = split(seq_len(nrow(mat)), cl)
align_to = align_to[names(align_to) != "0"]
align_to = align_to[names(align_to) %in% names(keywords)]
align_to## $`1`
## [1] 1 3 4 9 11 12 24 30 31 32 33 34 35 39 43 44 46 47
## [19] 51 58 74 78 81 85 87 89 91 92 97 98 99 100 103 104 107 111
## [37] 115 122 124 129 136 137 138 144 146 147 151 152 159 160 166 168 169 177
## [55] 178 185 188 190 192 201 202 208 214 216 227 231 234 244 246 247 248 251
## [73] 259 260 271 275 279 282 284 290 293 295 302 304 315 316 319 320 324 332
## [91] 347 348 351 352 355 356 363 370 371 372 375 382 399 400 406 407 408 411
## [109] 421 423 424 443 449 460 466 468 472 476 478 480 483 485 491 493 497 500
##
## $`3`
## [1] 6 18 19 21 22 23 25 27 36 37 48 49 53 55 59 60 63 64
## [19] 70 76 80 84 86 90 95 101 121 123 125 130 131 132 133 139 143 148
## [37] 149 150 153 155 156 174 176 191 194 196 197 198 199 204 209 210 211 212
## [55] 213 218 220 221 223 224 233 236 239 245 252 254 255 256 263 264 273 276
## [73] 278 287 292 294 297 299 301 310 313 318 321 328 329 334 336 364 368 381
## [91] 384 386 389 393 396 397 402 405 412 413 414 420 426 433 435 441 444 445
## [109] 447 451 459 461 463 464 470 471 474 477 479 482 488 492 495
##
## $`5`
## [1] 8 10 13 15 20 40 52 68 73 79 110 114 117 118 119 141 142 145 162
## [20] 167 171 179 183 186 200 207 222 226 238 249 262 265 266 267 268 272 280 281
## [39] 283 286 288 291 298 314 323 325 327 335 337 340 343 345 354 358 359 376 378
## [58] 380 385 387 388 391 392 415 425 432 436 439 442 446 448 450 456 457 458 467
## [77] 473 494
##
## $`2`
## [1] 2 5 26 28 56 57 62 65 69 77 94 102 105 109 127 134 154 158 161
## [20] 164 172 184 187 189 193 205 228 229 235 240 242 250 261 269 270 289 303 305
## [39] 309 326 330 331 342 344 346 357 360 361 367 373 377 398 401 417 422 427 429
## [58] 430 438 452 454 455 475 481 487 490 496 499
##
## $`6`
## [1] 16 17 38 42 50 54 66 82 83 88 116 126 128 135 165 170 206 215 217
## [20] 219 225 237 258 274 307 311 339 350 362 369 374 390 419 431 440 498
##
## $`4`
## [1] 7 14 72 203 312 403 462 484
##
## $`13`
## [1] 75 113 195 277 296 317 366
##
## $`15`
## [1] 106 175 232 257 306 308 453
##
## $`16`
## [1] 108 182 349 395 409 428 489
##
## $`11`
## [1] 67 93 140 300 353Next I construct a list of word cloud grob. Note I use scale_fontsize() to
map word frequency to font size.
fontsize_range = c(4, 16)
gbl = lapply(names(align_to), function(nm) {
kw = keywords[[nm]][, 1]
freq = keywords[[nm]][, 2]
fontsize = scale_fontsize(freq, rg = c(1, max(10, freq)), fs = fontsize_range)
word_cloud_grob(text = kw, fontsize = fontsize)
})
names(gbl) = names(align_to)
gbl## $`1`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.337]
##
## $`3`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.349]
##
## $`5`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.361]
##
## $`2`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.373]
##
## $`6`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.385]
##
## $`4`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.394]
##
## $`13`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.401]
##
## $`15`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.408]
##
## $`16`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.415]
##
## $`11`
## word_cloud[GRID.word_cloud.422]I calculate the height of each word cloud and use the maximal width of all grob as the width of the “linking annotation”. The heights and widths are added with 8pt as margins.
margin = unit(8, "pt")
gbl_h = lapply(gbl, function(x) convertHeight(grobHeight(x), "cm") + margin)
gbl_h = do.call(unit.c, gbl_h)
gbl_w = lapply(gbl, function(x) convertWidth(grobWidth(x), "cm"))
gbl_w = do.call(unit.c, gbl_w)
gbl_w = max(gbl_w) + marginThe use of convertHeight() and convertWidth() is mainly for simplying the unit objects.
panel_fun is defined as follows. The use of grid.lines() only draws the bottom,
right and top border of the viewport.
panel_fun = function(index, nm) {
# background
grid.rect(gp = gpar(fill = "#DDDDDD", col = NA))
# border
grid.lines(c(0, 1, 1, 0), c(0, 0, 1, 1), gp = gpar(col = "#AAAAAA"),
default.units = "npc")
gb = gbl[[nm]]
# a viewport within the margins
pushViewport(viewport(x = margin/2, y = margin/2,
width = grobWidth(gb), height = grobHeight(gb),
just = c("left", "bottom")))
grid.draw(gb)
popViewport()
}And the final heatmap with the word cloud annotations are as follows.
ht = ht + rowAnnotation(keywords = anno_link(align_to = align_to,
which = "row", panel_fun = panel_fun,
size = gbl_h, gap = unit(2, "mm"),
width = gbl_w + unit(5, "mm"), # 5mm for the link
link_gp = gpar(fill = "#DDDDDD", col = "#AAAAAA"),
internal_line = FALSE)) # you can set it to TRUE to see what happens
draw(ht, ht_gap = unit(2, "pt"))